One of the most powerful ways to improve business performance is combining business process management (BPM) strategies with Six Sigma strategies. BPM strategies emphasize process improvements and automation to drive performance, while Six Sigma uses statistical analysis to drive quality improvements. The two strategies are not mutually exclusive, however, and some savvy companies have discovered that combining BPM and Six Sigma can create dramatic results.
BPM Basics
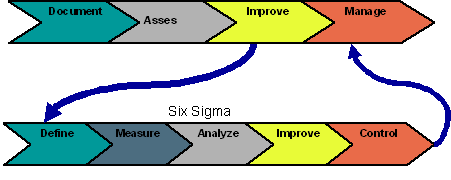
First, take a look at the basics of BPM. It uses a four step method to create better processes and improve performance. The steps are as follows:
- Document the process from start to finish, capturing each step along the way
- Assess the process performance and identify metrics, using findings as the basis for continuous process improvement
- Improve the process to improve quality, efficiency, customer satisfaction, etc.
- Manage the process through information flow, actions and related activities
![]()
BPM has a strong base in software applications to help streamline and automate processes. At the software level, BPM enables the links to multiple departments or groups that affect processes. At its highest level, BPM expands to an enterprise-wide system. This level combines software and IT aspects with management practices to address broad structural and systemic issues within a business or organization. Business practices and operations are examined from a value chain standpoint, paying close attention to how events in any part of the system have a ripple effect across the entire organization.
Six Sigma Basics
The basic concepts of Six Sigma were developed at Motorola in the 1980’s as they worked to improve the quality of their products and services. They have been refined and improved over the years by many successful companies. By implementing a systematic, rigorous routine, they were able to improve their services or products and increase customer satisfaction, thus increasing profits.Six Sigma approaches business processes from a highly analytical point of view. It incorporates five levels of activity:
- Philosophy – the enterprise-wide embrace of defect reduction by making decisions based on hard data and customer focus
- Focus on the Customer – meet or exceed their requirements/expectations.
- Metrics – statistical focus to make process outcomes 99.9997% defect free, otherwise expressed as 3.4 defects per million opportunities
- Methodology – structured approach to solving problems that uses specific tools and process mapping to achieve the metric goal
- Process based – the defects or errors introduced into products or services are based upon deficiencies in the processes
In short, Six Sigma allows an organization to reduce the variability in its products and services so that waste is reduced, efficiency is improved, and customer satisfaction is dramatically increased. Business problems are solved through rigorous application of data collection and analysis tools. The training that Six Sigma users receive is quite intensive, progressing through several increasingly sophisticated levels based on experience and accomplishment. Professional Six Sigma consultants and practitioners usually work to become certified at the various levels, increasing their ability to help guide development and implementation of Six Sigma methodology.
The methodology of Six Sigma is the key to its success. An organization follows a five step progression (DMAIC) that uses information and statistical analysis to address the achievement of operational goals. There are some differences in the five steps depending on whether they are used to improve an existing process or design a new process. The end goal, though, is always to achieve the standard metric of 99.9997% defect free performance.

- Define. The Define phase is concerned with the definition of project goals and boundaries, and the identification of issues that need to be addressed to achieve the higher (better) sigma level.
- Measure. The goal of the Measure phase of the Six Sigma strategy is to gather information about the current situation, to obtain baseline data on current process performance, and to identify problem areas.
- Analyze. The goal of the Analyze phase of the Six Sigma quality effort is to identify the root cause(s) of quality problems, and to confirm those causes using the appropriate data analysis tools.
- Improve. The goal of the Improve phase is to implement solutions that address the problems (root causes) identified during the previous (Analyze) phase.
- Control. The goal of the Control phase is to evaluate and monitor the results of the previous phase (Improve).
- Basically identify an area where there is a process problem, measure it, work out why there is a problem and then fix it.
Combining BPM and Six Sigma
- Methodology for improvement
- Six Sigma
- Methodology to prioritize the projects and close the gaps
Reduces process variation – improves process capability
- Lean Six Sigma
In addition to the Six Sigma methodology, there is an emphasis on removing non-value added work
With this basic understanding of BPM and Six Sigma in mind, it is easy to see how powerful it can be to combine the two practices. Their strengths complement each other and create a synergy that instills the entire operation with a focus on quality and performance.
The strength of BPM lies in its ability to automate processes and workflow through modeling and examination of inputs, outputs and performance. It is not as strong, however, in its ability to analyze data associated with very difficult or multifaceted problems. Six Sigma fills this gap by providing the statistical analysis needed to deal with complex problems.
The strength of Six Sigma lies in its rigorous approach to data collection and analysis. Through this methodology it can identify even the smallest opportunities for process improvement, maximizing an organization’s ability to institute necessary changes. It is not as strong, however, in its ability to monitor process improvements and ensure they are applied across the board. BPM fills this gap by providing tools to automate process improvements and connect those improvements across the entire organization.
Both BPM and Six Sigma represent significant commitments on the part of a business or organization, and they take time to implement thoroughly. Tremendous organizational change is often required, leading most companies to start with a single department or pilot project and expand their use over a multi-year period. It is well worth the time and effort, though, to generate the substantial business improvements that are typical with BPM and Six Sigma.

















