The Strategy Execution Process
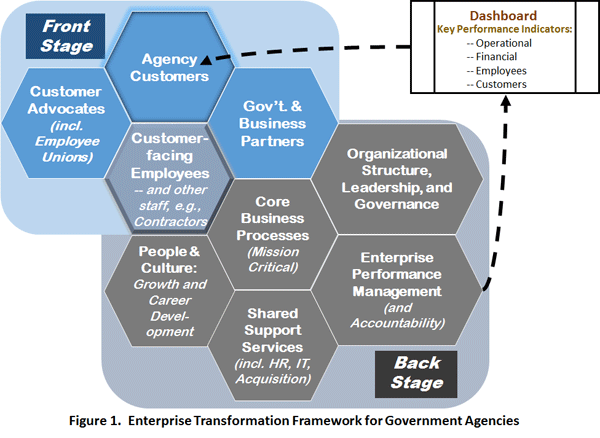
The strategy execution process provides a structured approach to clarifying, communicating, implementing, and managing strategy. The goal of this process is to ensure the organization focuses on developing high-value capabilities and making investments that optimize value. Most established and successful business architecture practices are deeply engaged in developing their organization’s strategy execution process though few have it completely implemented. Most are attempting to influence strategy from the bottom up.